Difference between revisions of "Angle bisector"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | For an [[angle]] <math> | + | For an [[angle]] <math>\angle ABC</math>, the angle bisector of <math>\angle ABC</math> is the line from B such that the angle between this line and <math>BC</math> is equal to the angle between this line and <math>AB</math>. |
<center>[[Image:Anglebisector.png]]</center> | <center>[[Image:Anglebisector.png]]</center> | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Geometry]] | ||
Revision as of 13:23, 4 December 2007
For an angle ![]() , the angle bisector of
, the angle bisector of ![]() is the line from B such that the angle between this line and
is the line from B such that the angle between this line and ![]() is equal to the angle between this line and
is equal to the angle between this line and ![]() .
.
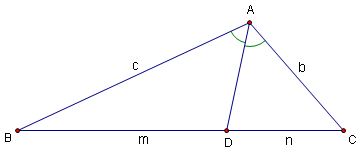
Features of Angle Bisectors
In a triangle, the angle bisectors (which are cevians) will all intersect at the incenter of the triangle.
See also
This article is a stub. Help us out by expanding it.










